Managing Insider Threat
A holistic approach to dealing with risk from within
Introduction
Insider threats in cyber security are threats posed by individuals from within an organization, such as current or former employees, contractors and partners. These individuals have the potential to misuse access to networks and assets to wittingly or unwittingly disclose, modify and delete sensitive information. Information at risk of being compromised could include details about an organization's security practices, customer and employee data, login credentials and sensitive financial records. The nature of insider threats means that traditional preventative security measures are often ineffective.
Traditional security measures tend to focus on external threats and are not always capable of identifying an internal threat emerging from inside an organization.
Types of insider threats include:
⦁ Malicious insider
Someone who maliciously and intentionally abuses legitimate credentials, typically to steal information for financial or personal incentives. They have an advantage over other attackers because they are familiar with the security policies and procedures of an organization, as well as its vulnerabilities.
⦁ The Negligent
An innocent pawn who unknowingly exposes the system to outside threats. This is the most common type of insider threat, resulting from mistakes, such as leaving a device exposed or falling victim to a scam.
⦁The Accidental
Accidental insider threat can be equally risky to the organization and is unfortunately quite common, accounting for 25% of data breaches in 2017. These are employees, vendors and partners with the best of intentions, but may accidentally click a link, forgo company policy, or accidentally leak information outside the organization.
Top 4 insider threat actors
Some cyber security experts believe that negligent and malicious employees are the most common actors in insider attacks. For example, in its 2019 Insider Threat Report [PDF], Verizon placed careless workers and misuse of assets at the top of their threat actors list. At the same time, they didn’t even mention privileged users. However, most of the cyber security community thinks otherwise. Cyber security Insiders surveyed [PDF] security professionals to identify the riskiest types of insiders. Here’s what types of users most of them consider the most dangerous:
⦁ Privileged users and administrators
These users are particularly threatening since they hold all the keys to the organization’s infrastructure and sensitive data. Because of their high level of access, harmful activity by privileged users is difficult to detect as they don’t break any cyber security rules when accessing sensitive resources.
⦁ Regular employees
Regular users are not so dangerous compared to privileged users, but they still can harm an organization. For instance, they can misuse corporate data, install unauthorized applications, send confidential emails to the wrong address, become a victim of a phishing attack, etc.to detect as they don’t break any cyber security rules when accessing sensitive resources.
⦁ Third parties and temporary workers
Vendors, business partners, and temps may not follow cyber security rules and practices implemented in your organization or may violate them unknowingly. Also, hackers can breach a third-party vendor with a low level of security to get inside your protected perimeter.
⦁ Privileged business users and executives
C-level executives have access to the most confidential and sensitive information about an organization. This category of users may abuse their knowledge for insider trading, personal gain, or corporate or government infiltration.
Why Insider Thefts are such Big Deal?
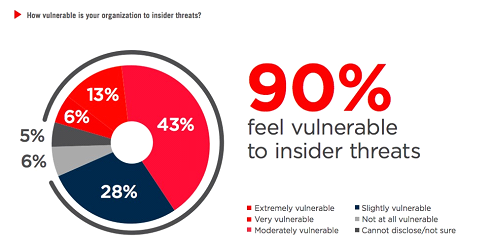
Insiders have direct access to data and IT systems, which means they can cause the most damage. According to a 2015 Intel Security study, insider threat actors were responsible for 43% of attacks, split evenly between malicious and unintentional actors. According to the IBM X-Force 2016 Cyber Security Intelligence Index, insider cyber security threats are an even bigger problem. From 2015 to 2016, the percentage of attacks carried out by all insiders grew from 55% to 60% according to the study. Of those, about 73.6% were carried out by malicious insiders — or 44.5% of total attacks. Insider threat mitigation is difficult because the actors are trusted agents, who often have legitimate access to company data. As most legacy tools have failed us, many cyber security experts agree that it is time to move on.
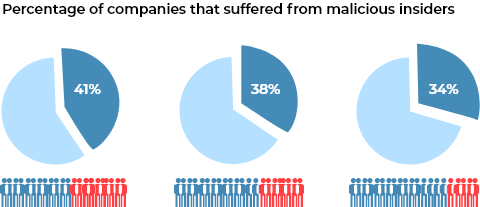
A lot of cyber security companies develop their strategies around preventing external threats. However, sometimes the worst attacks come from within.
Here are a few key benefits to looking into insider threat detection:
Monitoring and Reporting: Depending on the software or cyber security companies you invest in; insider threat detection should have some level of quick monitoring and reporting. As with other cyber security threats, if you are unable to make sense of the threat detections, it will be hard to do much about them.
Identify Patterns: Insider threats often come in patterns. If you have a way to identify and monitor internal breaches, it can help you begin to recognize the patterns within your own organization. This can help you make your company stronger against existing and future vulnerabilities.
Use Cases
Applying a better User Access Management Program:
User access management program is essential for insider threat detection. A report from the Ponemon Institute revealed that 62% of end users say they have access to company data they shouldn’t see. By following the least privilege model, all of your employees will only have access to information required to perform their jobs – no more and no less. This helps prevent data loss by restricting unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Monitoring Employees on their Usage for Abnormal Behavior:
Tools like Machine Learning (ML) applications can help analyze the data stream and prioritize the most relevant alerts. You can use digital forensics and analytics tools like User and Event Behavior Analytics (UEBA) to help detect, analyze, and alert the security team to any potential insider threats. User behavior analytics can establish a baseline for normal data access activity, while database activity monitoring can help identify policy violations.
Authentication
The bulk of insider threats facing businesses are due to negligence. While the workforce can be trained on cyber security awareness and so on, one cannot rule out possibilities of human error from time to time. Cyber security is about eliminating risks, which includes reducing the attack surface; if a breach does occur, it can be contained easily. In authentication, this can be implemented by using the least privilege principle. Least privilege means that no worker gains access to more data than is needed to perform their tasks at any point. In addition to identity verification, Risk Based Authentication (RBA) collects information about a user’s location, device, time of access, etc. to determine that no breach is being attempted. Avoiding two-factor authentication, RBA estimates a risk score based on login behavior.
Monitoring Employees on their Usage for Abnormal Behavior:
You won’t be able to detect insider threats without monitoring your employees. In order to make employee monitoring effective, you should first establish a baseline of normal behavior – their user access level, hours usually worked, files usually opened and downloaded, etc.
Then, look out for signs of abnormal behavior such as:
Copying information unrelated to their jobs
Initiating unauthorized file transfers
Installing unauthorized applications
Logging into your network at odd hours
Making unauthorized access onto Servers
Once an employee behaves abnormally, immediately intervene and find out why they’re doing what they’re doing before they cause any damage.
The Cost Factor
The total cost of an insider threat includes three components:
-
Direct cost — Money needed to detect, mitigate, investigate, and remediate the breach
-
Indirect cost — The value of resources and employee time spent dealing with the incident
Lost opportunity cost — Losses in potential profits because of the attack
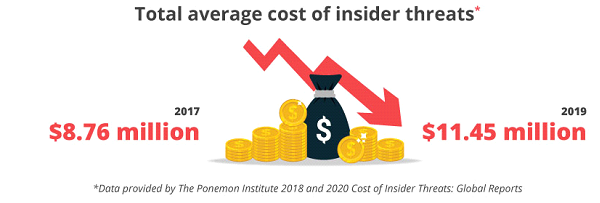
And these costs keep rising by the year.
The Ponemon Institute conducted two studies on the cost of insider threats: in 2018 and in 2020. According to their reports, the total average cost of a threat increased by 31% between 2017 and 2019, from $8.76 million to $11.45 million. Companies from North America suffer the most from insider attacks and their consequences: the average cost in this region increased from $11.1 million to $13.3 million. The average total spending on a single insider threat incident (including monitoring, investigation, escalation, incident response, containment, ex-post analysis, and remediation)also went up from $513,000 to $756,760
How
Iraje PAM Solution
helps in
Insider Threat Detection
Iraje PAM Solution helps in Manage, Monitor and Control privileged access to critical assets.
Key Features of Iraje PAM:
Managing the identities and accesses of all privileged users within the enterprise; Providing privileged users, role-based access with single sign on to all enterprise assets
Monitor privileged user accesses to critical enterprise assets. Watch live privileged user sessions and terminate them if necessary. Replay recorded sessions and search commands within recorded sessions. This gives ability to get visibility and do forensics very quickly.
Added level of authentications to prevent identity attacks. Solution supports all types of second factor authentication including Biometrics, Email/SMS OTP, App Based OTP, Soft/Hard Tokens, Cisco DUO, Entrust, Twilio Auth, and so on out of the box
Additional Features of Iraje PAM:
Restrict privileged users having admin access from executing sensitive commands. Control privileged accesses and prevent incidents and data breaches.
Ability to discover hidden devices, hidden admins, active ports and password sync out of box without any agents.
-
Solution provides real time security event alerts. These alerts help the security team to get granular visibility on events that are security incidents and potential data breaches. The reports are available on demand or on schedule on email (viz. Bypass Alerts, Maker Checker Alerts, Server Access Alerts, Restricted Command Executed, Show Password Alerts, and so on.
Integrated DLP feature for gaining visibility and control of your data right away for Identifying, monitoring, and preventing data loss. DLP helps in implementing controls for protection, visibility, and enforcement.
IP Based PAM Dashboard Login & IP Based Two Factor Authentication White-listing on PAM Dashboard to end users out of the box
Solution provides all types of slice and dice reports that help security teams analyze data and security incidents. These reports also help in Behavioral Analytics of users. These Reports are available to meet requirements of different regulatory standards like PCI, SOX, HIPPA, ISO27001, GDPR and more.